Diabetes and insulin resistance are two commonly discussed medical conditions that have a significant impact on individuals’ overall health. These conditions are often linked to the development of cardiovascular diseases, making it crucial for individuals to understand how they can affect their health. In this article, we will dive deep into the causes and risk factors of diabetes and insulin resistance, as well as how these conditions can lead to cardiovascular diseases. Whether you have been diagnosed with diabetes or insulin resistance or are looking to prevent these conditions, this article will provide valuable insights and information. So, let’s explore the world of diabetes and insulin resistance and gain a better understanding of their impact on our health.
Diabetes and insulin resistance are two closely related conditions that can have a significant impact on cardiovascular health. Understanding the connection between these two conditions is crucial for individuals looking to improve their heart health and prevent serious conditions like heart disease, heart attacks, and strokes.
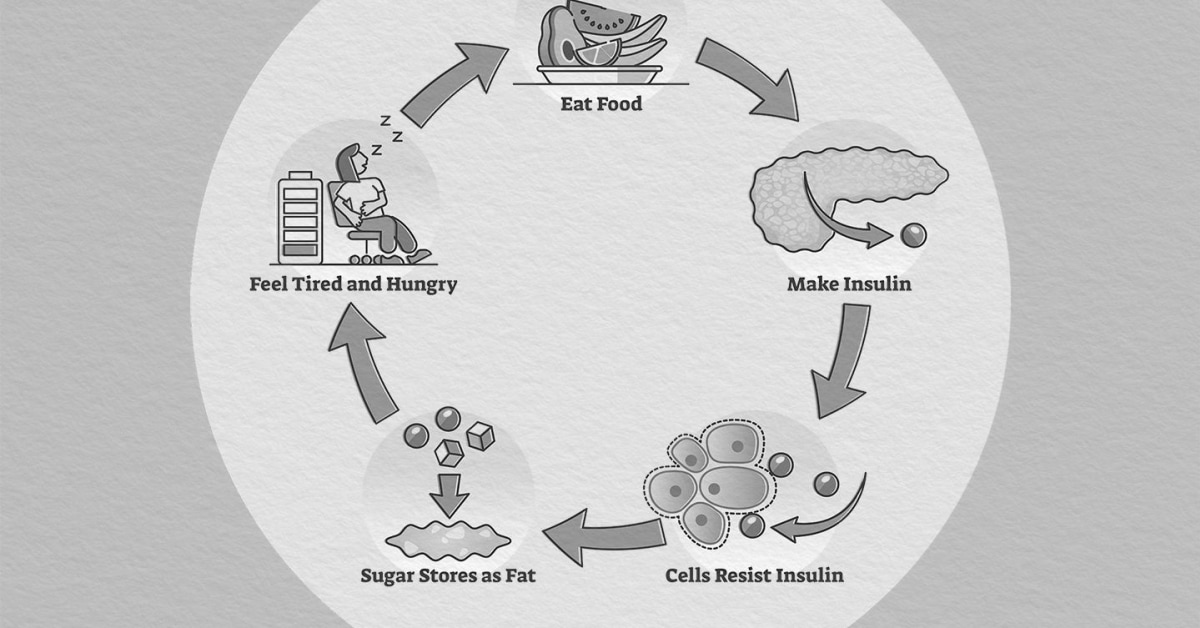
Firstly, it is important to understand what diabetes and insulin resistance are. Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects how your body uses glucose (sugar). Insulin resistance, on the other hand, is a condition where your body becomes less sensitive to the effects of insulin, leading to higher levels of glucose in the blood. Both of these conditions can increase your risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
In this section, we will discuss the different types of diabetes, including type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes, as well as the causes and risk factors for each type. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. On the other hand, type 2 diabetes is caused by a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors, such as obesity and physical inactivity. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Insulin resistance develops when the cells in your body become less responsive to insulin, which is responsible for regulating blood sugar levels. This can be caused by genetic factors or lifestyle factors such as obesity, physical inactivity, and an unhealthy diet. Insulin resistance can lead to high blood sugar levels and increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes and insulin resistance are diagnosed through various blood tests that measure blood sugar levels and insulin levels in the body. Treatment for both conditions involves managing blood sugar levels through lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, as well as medication such as insulin injections or oral medications.
In conclusion, understanding the causes and risk factors of diabetes and insulin resistance is crucial for maintaining good cardiovascular health. By making lifestyle changes and managing these conditions, individuals can reduce their risk of developing serious cardiovascular diseases and improve their overall well-being.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diabetes and insulin resistance can often go undetected in individuals, as symptoms may not appear until the condition has progressed. Therefore, early detection is crucial in managing these conditions and reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
For diabetes, a diagnosis is typically made through a blood test to measure blood sugar levels. If the results show higher than normal levels, further testing may be done to determine the type of diabetes and the best course of treatment.
Insulin resistance is a bit more complex to diagnose, as there is no single test that can definitively diagnose it. However, doctors may use a combination of tests such as fasting glucose levels, insulin levels, and glucose tolerance tests to make a diagnosis.
Once diagnosed, it is important for individuals to work closely with their healthcare team to manage their diabetes and insulin resistance. This may involve making lifestyle changes such as following a healthy diet, maintaining a regular exercise routine, and monitoring blood sugar levels. In some cases, medication may also be prescribed to help regulate blood sugar levels.
It is also important for individuals with these conditions to regularly monitor their cardiovascular health through check-ups with their doctor. This can help catch any potential issues early on and allow for proper management.
Types of Diabetes
Understanding the Different Types of Diabetes.
Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects how the body uses glucose, or blood sugar. There are three main types of diabetes: type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes. Each type has its own unique causes and risk factors, but all can contribute to the development of insulin resistance and cardiovascular disease.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. This type of diabetes is typically diagnosed in childhood or adolescence and requires lifelong insulin therapy.
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for 90-95% of all cases. It occurs when the body becomes resistant to the effects of insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels. Risk factors for type 2 diabetes include obesity, physical inactivity, family history, and ethnicity.
Gestational diabetes is a form of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy, typically in the second or third trimester. It can increase the risk of complications during pregnancy and may also increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
It’s important to understand the different types of diabetes and their causes in order to take steps towards prevention and management. By making healthy lifestyle choices and working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals can reduce their risk of developing insulin resistance and cardiovascular disease.
Causes and Risk Factors
Diabetes and insulin resistance are two closely related conditions that can have a significant impact on cardiovascular health. While genetics and family history play a role in the development of these conditions, there are also several other factors that can contribute to their onset.
Unhealthy Diet: A diet high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can increase the risk of both diabetes and insulin resistance. This type of diet can lead to weight gain and obesity, which are major risk factors for these conditions.
Lack of Exercise: Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining a healthy weight and preventing chronic diseases like diabetes and insulin resistance. Lack of exercise can also contribute to insulin resistance by reducing the body’s sensitivity to insulin.
Obesity: As mentioned earlier, obesity is a significant risk factor for both diabetes and insulin resistance. Excess body fat, especially around the waist, can increase insulin resistance and make it more difficult for the body to regulate blood sugar levels.
High Blood Pressure: People with high blood pressure are at an increased risk for developing diabetes and insulin resistance. This is because high blood pressure can damage the blood vessels and decrease the body’s ability to use insulin effectively.
Sleep Deprivation: Lack of quality sleep can disrupt the body’s hormone levels and increase the risk of diabetes and insulin resistance. It is essential to aim for 7-9 hours of sleep each night to maintain good overall health.
Impact on Cardiovascular Health
Diabetes and insulin resistance are two closely related conditions that can have a significant impact on cardiovascular health. These conditions can lead to a variety of serious complications, including heart disease, heart attacks, and strokes. Understanding the connection between diabetes, insulin resistance, and cardiovascular diseases is crucial for individuals looking to improve their heart health and prevent these serious conditions.
Insulin resistance occurs when the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. This leads to higher levels of glucose in the blood, which can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of heart disease. Diabetes, on the other hand, is a chronic disease where the body either does not produce enough insulin or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. This also results in high blood sugar levels and can lead to damage to the heart and blood vessels.
The link between diabetes, insulin resistance, and cardiovascular diseases lies in the fact that both conditions can cause damage to blood vessels and increase the risk of heart disease. Over time, high blood sugar levels caused by diabetes and insulin resistance can damage the lining of blood vessels, making them more prone to plaque buildup. This can lead to atherosclerosis, a condition where plaque builds up in the arteries and restricts blood flow to the heart.
The damage to blood vessels caused by diabetes and insulin resistance can also increase the risk of blood clots forming, which can block blood flow to the heart and lead to a heart attack or stroke. Additionally, these conditions can also lead to high blood pressure, another major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases.
It is important for individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance to manage their condition carefully and take steps to reduce their risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. This may include making lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and monitoring blood sugar levels. Working closely with a healthcare provider can also help individuals manage their condition and reduce their risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular complications.
In conclusion, diabetes and insulin resistance are serious conditions that can have a significant impact on cardiovascular health. It is important for individuals to understand the causes and risk factors of these conditions, as well as how they can be managed and prevented. By making lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise, individuals can improve their heart health and reduce their risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.