Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a common cardiovascular condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a serious and potentially life-threatening disease that occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked due to a buildup of plaque. This can lead to a restriction of blood flow to the heart, causing symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue.
Understanding the symptoms and warning signs of CAD is crucial for early detection and prevention of further complications. In this article, we will delve into the various symptoms and warning signs of CAD and provide valuable information on how to recognize them. Whether you have been diagnosed with CAD or are simply looking to learn more about this condition, this article will serve as a comprehensive guide to help you understand and manage your symptoms.
Join us as we explore the ins and outs of CAD and equip you with the knowledge you need to take control of your health.
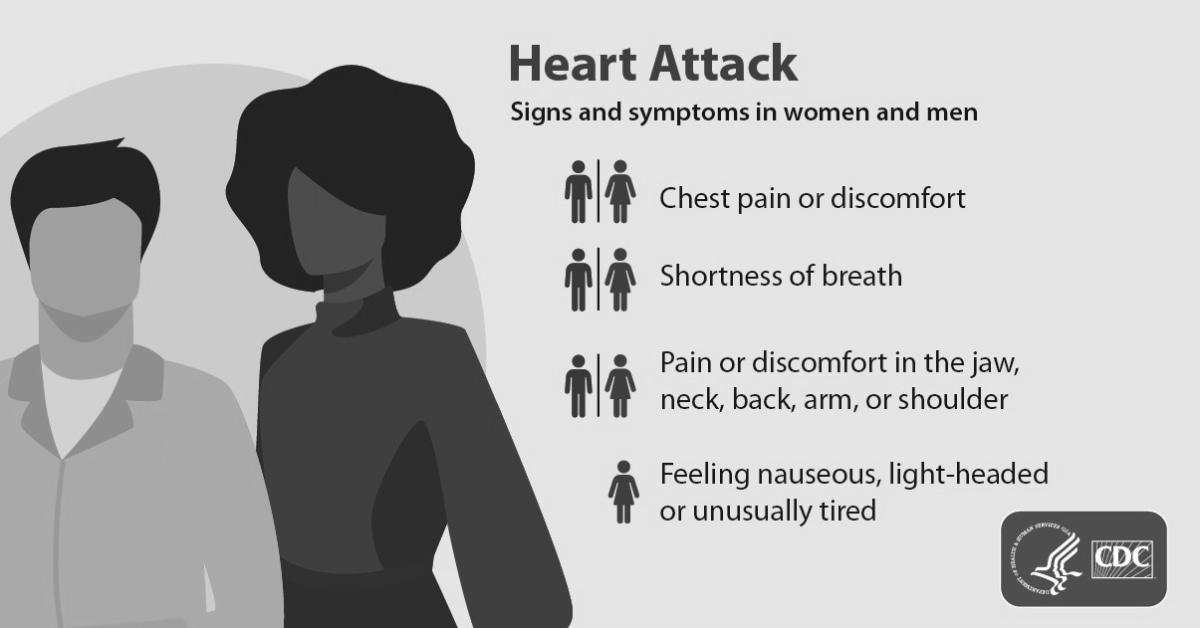
To begin, let’s discuss what CAD is and how it affects the body. Coronary artery disease occurs when there is a buildup of plaque in the arteries that supply blood to the heart. This plaque can eventually block blood flow to the heart, leading to a heart attack or other serious complications. The most common symptom of CAD is chest pain or discomfort, also known as angina. This can feel like pressure or tightness in the chest, and may also be accompanied by shortness of breath, sweating, or dizziness. Other symptoms may include fatigue, nausea, or pain in the arm, back, neck, or jaw. It is important to note that not everyone with CAD will experience these symptoms, and some may only experience them during physical activity or times of stress.
Risk Factors for CAD
In order to prevent CAD, it is important to understand the risk factors that can increase your chances of developing this condition. These risk factors include:
- High blood pressure: This is a major risk factor for CAD, as it puts a strain on your heart and can damage your arteries.
- High cholesterol levels: High levels of cholesterol can lead to plaque buildup in your arteries, increasing your risk of CAD.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing CAD, as high blood sugar levels can damage the walls of the arteries.
- Smoking: Smoking damages the lining of your arteries, making it easier for plaque to build up and increasing your risk of CAD.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese puts extra strain on your heart and increases your risk of developing CAD.
It is important to address these risk factors in order to prevent CAD and maintain a healthy cardiovascular system. This can be done through lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and quitting smoking. Regular check-ups with your doctor can also help monitor and manage these risk factors.
Preventative Measures for CAD
In order to prevent the development of coronary artery disease (CAD) and maintain a healthy heart, there are several lifestyle changes that you can make. These changes not only reduce your risk of developing CAD, but also improve your overall heart health. By implementing these preventative measures, you can take control of your health and reduce your risk of serious cardiovascular issues.
1. Maintain a healthy diet: Eating a balanced and nutritious diet is crucial for maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system. Aim for a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoid foods high in saturated and trans fats, as well as excessive amounts of salt and sugar.
2. Exercise regularly: Regular physical activity helps keep your heart strong and healthy. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise, such as brisk walking or cycling, five days a week.
3. Avoid smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for CAD and other cardiovascular diseases. If you currently smoke, consider quitting or seeking help to quit.
4. Manage stress: Chronic stress can have negative effects on your heart health. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, meditation, or spending time with loved ones.
5. Monitor your blood pressure and cholesterol levels: High blood pressure and cholesterol can increase your risk of developing CAD. Make sure to regularly check these levels and take steps to lower them if needed.
6. Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can damage the heart muscle and increase the risk of CAD. If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation.
In conclusion, understanding the symptoms and warning signs of CAD is crucial for maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system. By recognizing these signs and taking preventative measures, you can reduce your risk of developing serious health issues such as heart disease, heart attacks, and strokes. Remember to consult with your doctor if you experience any symptoms of CAD, as early detection and treatment is key in managing this condition.