Neurodegenerative diseases are becoming increasingly prevalent in our aging population, with conditions such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s affecting millions of individuals worldwide. While these diseases may present with different symptoms and progression patterns, they all share one commonality – the role of inflammation in their development and progression. Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury or infection, but when it becomes chronic and uncontrolled, it can lead to widespread damage and contribute to the degeneration of neurons in the brain. In this article, we will delve into the mechanisms of neurodegeneration and explore the crucial role that inflammation plays in this process. By understanding the relationship between inflammation and neurodegeneration, we can potentially uncover new treatment strategies and improve the quality of life for those affected by these debilitating diseases. So let’s dive into the complex and fascinating world of neurodegeneration and discover the vital role that inflammation plays in this intricate process.
To understand the link between inflammation and neurodegeneration, it is important to first understand the basics of neurodegenerative diseases. These conditions involve the progressive loss of structure or function of brain cells, leading to cognitive and physical decline. In recent years, research has shown that chronic inflammation plays a key role in the development and progression of many neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
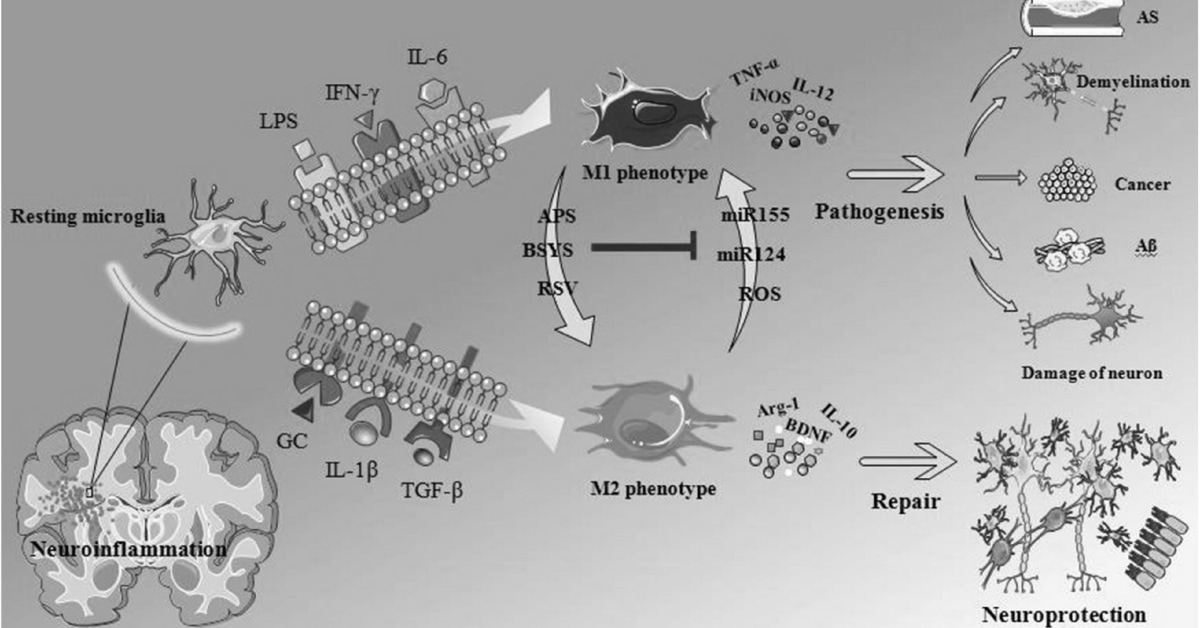
One of the main ways inflammation contributes to neurodegeneration is through the activation of immune cells in the brain, called microglia. When triggered by inflammation, these cells release harmful molecules that can damage neurons and interfere with their normal functioning. This can lead to a cascade of events that ultimately result in cell death and loss of brain tissue.
In addition, chronic inflammation can also disrupt the blood-brain barrier, which normally protects the brain from harmful substances in the blood. This allows inflammatory molecules to enter the brain and cause damage, further contributing to neurodegeneration.
While inflammation has been shown to play a significant role in neurodegeneration, it is important to note that it is not the sole cause. Other factors such as genetics, lifestyle choices, and environmental factors also play a role in the development of these diseases. However, understanding the impact of inflammation can provide valuable insights for potential treatments and preventive measures.
One potential treatment approach is targeting the inflammatory response itself. This can be done through medications that suppress inflammation or by addressing underlying conditions that may be causing chronic inflammation in the body. In addition, lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet and regular exercise can also help reduce inflammation and potentially slow down the progression of neurodegenerative diseases.
It is also important to note that not all inflammation is harmful. Acute inflammation, which is a normal response to injury or infection, can actually be beneficial for brain health. It is only when inflammation becomes chronic and excessive that it becomes problematic.
Overall, the role of inflammation in neurodegeneration is complex and multifaceted. While more research is needed to fully understand its mechanisms, it is clear that addressing chronic inflammation can have a significant impact on brain health and potentially slow down the progression of neurodegenerative diseases.
Potential Treatments for Neurodegeneration
Inflammation plays a key role in the progression of neurodegenerative diseases. Chronic inflammation can lead to a worsening of symptoms and further damage to the brain. Therefore, addressing chronic inflammation is an important aspect of treating neurodegeneration.
One potential treatment for neurodegeneration is through the use of anti-inflammatory drugs. These medications can help reduce the levels of inflammation in the brain, potentially slowing down the progression of the disease. However, these drugs may also have side effects and may not be suitable for everyone.
Another approach to addressing chronic inflammation is through lifestyle changes. Eating a healthy diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, can help reduce inflammation in the body. Regular exercise can also have anti-inflammatory effects, as well as reducing stress levels which can contribute to inflammation.
In addition, some natural supplements have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties and may be beneficial in treating neurodegeneration. These include curcumin, resveratrol, and omega-3 fatty acids. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements.
Overall, addressing chronic inflammation is crucial in the treatment of neurodegeneration. Whether through medication, lifestyle changes, or natural supplements, reducing inflammation can help slow down the progression of the disease and improve overall brain health.
Understanding Neurodegenerative Diseases
Neurodegenerative diseases are a group of disorders that primarily affect the neurons in the brain. These diseases can lead to progressive loss of function, impairment of cognitive abilities, and even death. Some common neurodegenerative diseases include Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Although these diseases have different causes and symptoms, they all share a common underlying factor – inflammation.
When the brain is injured or infected, immune cells called microglia release inflammatory molecules to fight off the threat. This acute inflammation is a necessary and helpful response. However, when the inflammation persists for a long time, it can become chronic and damaging to the brain cells. The constant presence of inflammatory molecules can lead to the death of neurons, which is the main cause of neurodegeneration.
Inflammation can also contribute to the formation of protein clumps or plaques in the brain, which are characteristic features of many neurodegenerative diseases. These clumps can interfere with neuronal communication and further damage brain cells. Additionally, chronic inflammation can also disrupt the blood-brain barrier, a protective barrier that regulates the entry of substances into the brain. This disruption can allow harmful molecules to enter the brain and cause further damage.
Overall, understanding the role of inflammation in neurodegeneration is crucial in finding effective treatments and preventive measures for these debilitating diseases. By targeting inflammation and finding ways to reduce its harmful effects, we may be able to slow down or even stop the progression of neurodegeneration. With ongoing research and advancements in this field, we hope to gain a better understanding of the complex mechanisms involved in neurodegenerative diseases and develop more targeted and effective treatments.
The Link between Inflammation and Neurodegeneration
Inflammation is a natural response of the body to injury or infection. However, when this response becomes chronic, it can lead to neurodegeneration – the progressive loss of function and structure of neurons in the brain. The connection between inflammation and neurodegeneration has been a topic of interest for researchers in recent years, as it offers a potential pathway for understanding and treating various neurodegenerative diseases.
Studies have shown that chronic inflammation can contribute to the development and progression of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s. Inflammation triggers the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which can damage neurons and disrupt their communication with each other. This can lead to cognitive decline, motor dysfunction, and other symptoms associated with these diseases.
But what exactly is the link between inflammation and neurodegeneration? While the exact mechanisms are still being studied, it is believed that chronic inflammation can directly damage neurons and contribute to their dysfunction. It can also activate immune cells in the brain, such as microglia, which can produce toxic substances that harm neurons.
Additionally, chronic inflammation can also disrupt the blood-brain barrier, which is responsible for regulating the entry of substances into the brain. This can allow harmful molecules and immune cells to enter the brain, further exacerbating neurodegeneration.
Uncovering the connection between inflammation and neurodegeneration is crucial for developing effective treatments for these diseases. By targeting inflammation, researchers hope to slow down or even prevent the progression of neurodegeneration. This could involve developing anti-inflammatory drugs or finding ways to regulate the body’s immune response to reduce chronic inflammation.
In conclusion, chronic inflammation plays a significant role in neurodegeneration. Understanding the link between the two can provide valuable insights into the development and progression of various neurodegenerative diseases. By further exploring this connection, we can pave the way for new treatments and ultimately improve brain health for those affected by these conditions.
In conclusion, chronic inflammation plays a significant role in neurodegenerative diseases. By understanding its impact on brain health, we can explore potential treatments and preventive measures to slow down the progression of these conditions. However, it is important to note that more research is needed to fully understand the complex mechanisms at play. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and addressing underlying conditions that may contribute to chronic inflammation can also play a crucial role in promoting brain health.